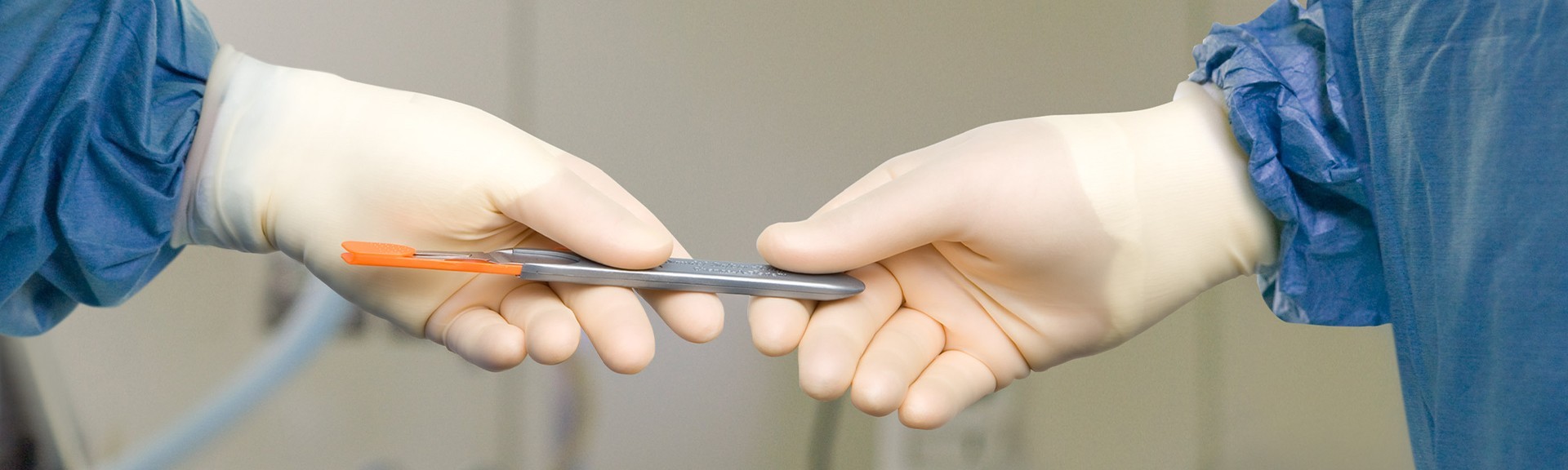
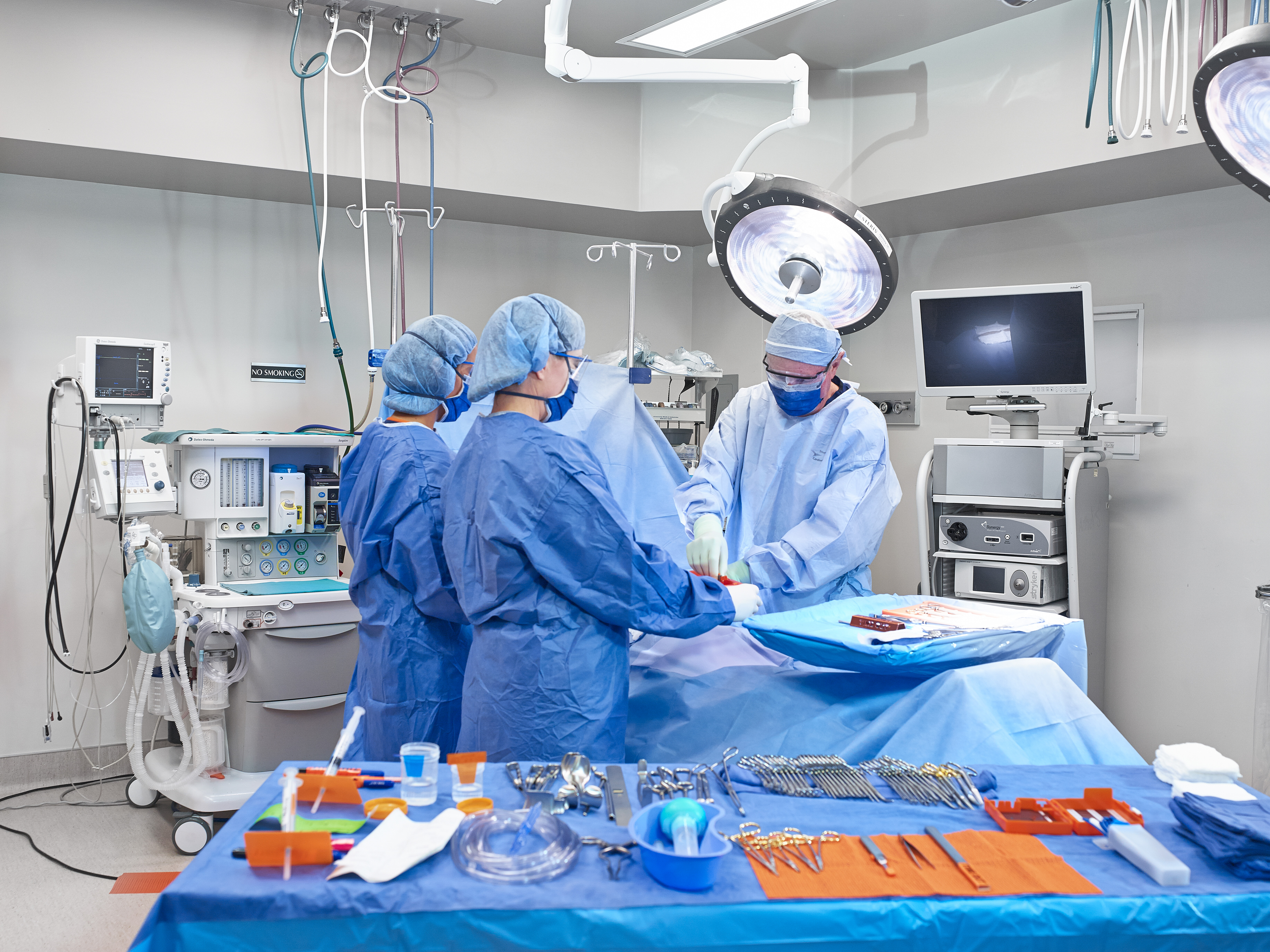
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), each year in the U.S. approximately 385,000 sharps-related injuries are sustained by hospital-based personnel.1 Up to 70% of nurses and doctors have experienced a needlestick or sharp injury, with nearly 44% occurring in the operating room and almost 24% occurring in patient or exam rooms.2
Register Now and view AnsellCARES Partners in Protection webinar:
A Manager's View on Championing Safety in the Surgical Environment
Presented by:

Victoria Tyde, BSN, RN, CNOR,
Former OR Manager
Former OR Manager
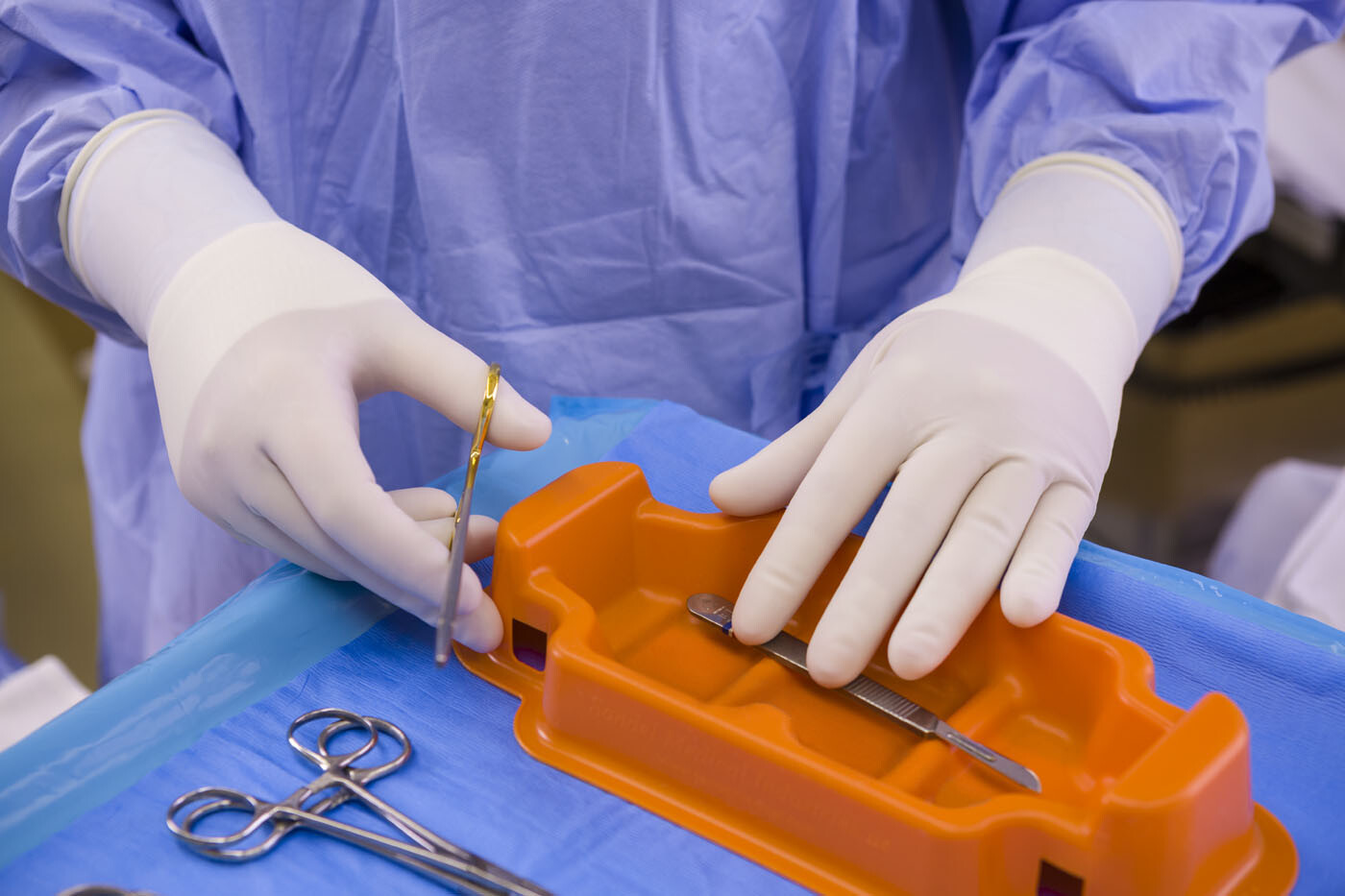
The top 3 most frequent devices causing injury include:
- 24% Suture
- 17% Disposable Syringe
- 7% Blood Collection/Winged Needle or Tube Holder2
There are many ways to prevent sharps injuries: double gloving, using correct technique, creating a neutral zone, and using alternative engineering control methods.3